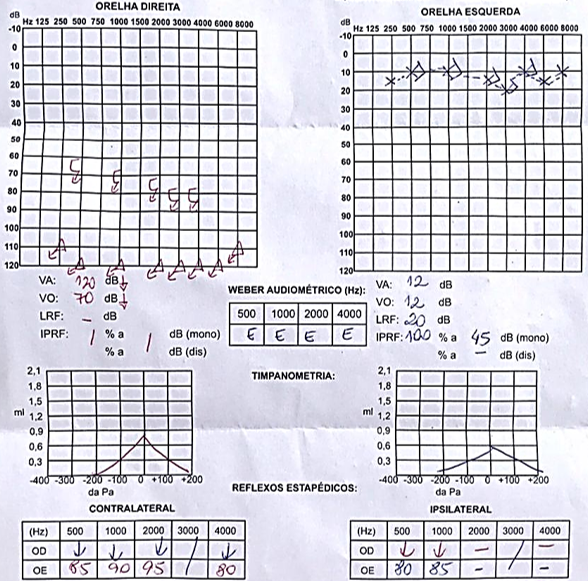
Paciente do sexo masculino, 51 anos. (Male 51 y)
Paciente refere que há seis meses começou com hipoacusia e zumbido no ouvido direito. Em seguida apresentou desequilíbrio. Relata que com movimentos da cabeça há atraso na imagem. Sente esse atraso para qualquer movimento da cabeça e piora quando está mais cansado e também no final do dia.
Patient reports that six months ago he started with hearing loss and tinnitus in his right ear. Then he presented an imbalance. He reports that with head movements there is delay in the image. He feels this delay for any head movement and it gets worse when he is more tired and also at the end of the day.
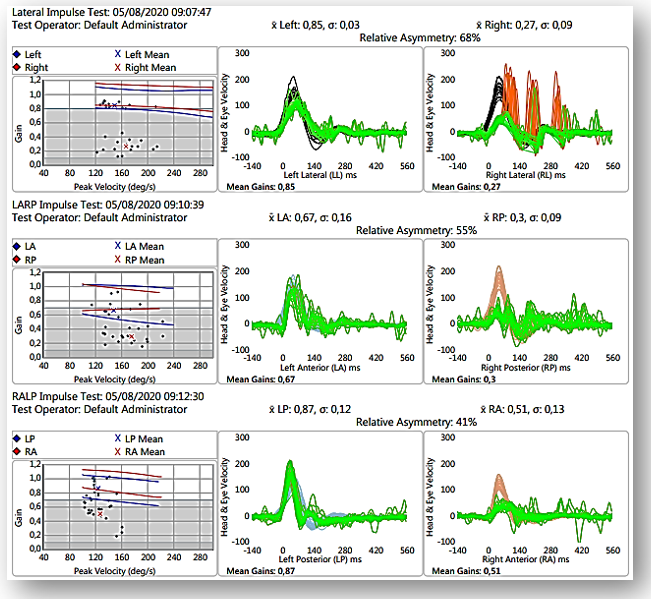
VHIT : Os achados são compatíveis com hipofunção de todos os canais semicirculares do lado direito.
O padrão das sacadas do canal lateral direito é um padrão organizado, inclusive com dois “picos” de sacadas de tipo overt. Esse padrão costuma ser encontrado na hipofunção crônica.
VHIT: The findings are compatible with hypofunction of all semicircular canals on the right side. Gatthered pattern saccades on the right lateral canal
, including two “peaks” of overt saccades. This pattern is usually found in chronic hypofunction.
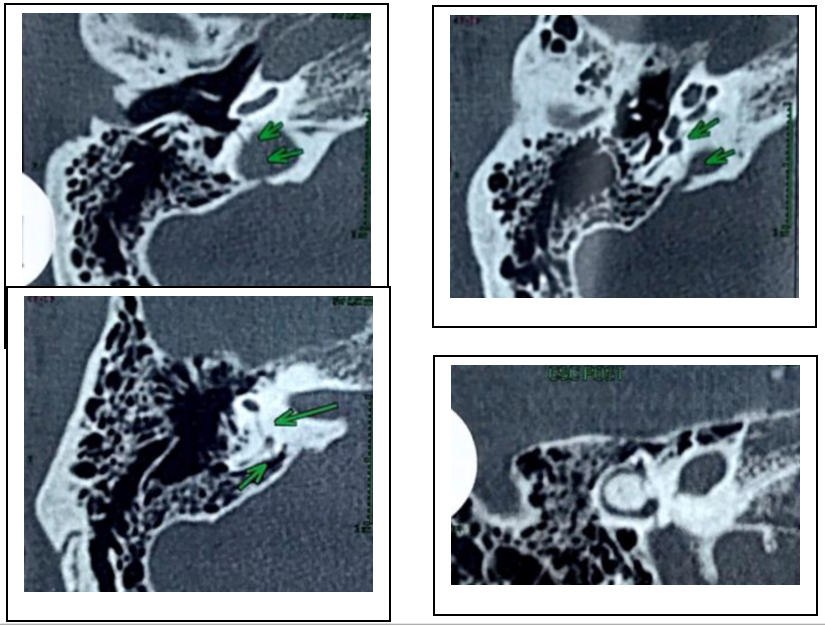
TOMOGRAFIA
Traços oblíquos de fratura comprometendo a porção petrosa do osso temporal direito, interceptando as margens do foramen jugular, o aqueduto vestibular, vestíbulo e canais semicirculares correspondentes, sem desalinhamento ósseo, com extensão à face labiríntica da caixa timpânica.
Tênues focos de calcificação na topografia do labirinto membranoso em correspondência com o canal semicircular lateral direito com redução de sua amplitude.
Aspecto tomográfico sugere labirintite ossificante à direita, possivelmente de etiologia pós-traumática.
CT: Oblique fracture lines affecting the petrous portion of the right temporal bone, intercepting the margins of the jugular foramen, the vestibular aqueduct, vestibule and corresponding semicircular canals, without bone misalignment, with extension to the labyrinthine face of the tympanic cavity.
Faint foci of calcification in the topography of the membranous labyrinth in correspondence with the right lateral semicircular canal with a reduction in its amplitude.
Tomographic aspect suggests ossifying labyrinthitis on the right, possibly of post-traumatic etiology.
A labirintite ossificante, também conhecida como ossificação labiríntica, representa ossificação patológica do labirinto membranoso em resposta a um insulto ao ouvido interno.
Geralmente está associada à perda auditiva neurossensorial profunda e às vezes pode estar associada a tonturas e / ou vertigens. É a causa mais comum de perda auditiva neurossensorial adquirida em crianças.
A doença é mais comumente o resultado final de labirintite supurativa prévia, seja relacionada à otomastoidite (etiologia timpanogênica) ou meningite (etiologia meningogênica) . Outras causas incluem cirurgia ou trauma do osso temporal , doença autoimune do ouvido interno e doença falciforme .
Labyrinthitis ossificans, also known as labyrinthine ossification, represents pathological ossification of the membranous labyrinth as a response to an insult to the inner ear.
It is usually associated with profound sensorineural hearing loss, and may sometimes be associated with dizziness and/or vertigo. It is the most common cause of acquired sensorineural hearing loss in children.
The disorder is most commonly the end result of prior suppurative labyrinthitis, either related to otomastoiditis (tympanogenic etiology) or meningitis (meningogenic etiology). Other causes include temporal bone surgery or trauma, autoimmune inner ear disease , and sickle cell disease .
Ref: (https://radiopaedia.org/articles/labyrinthitis-ossificans)